- April 18, 2024
Factors Which Can Increase the Risk of Oral Cancer
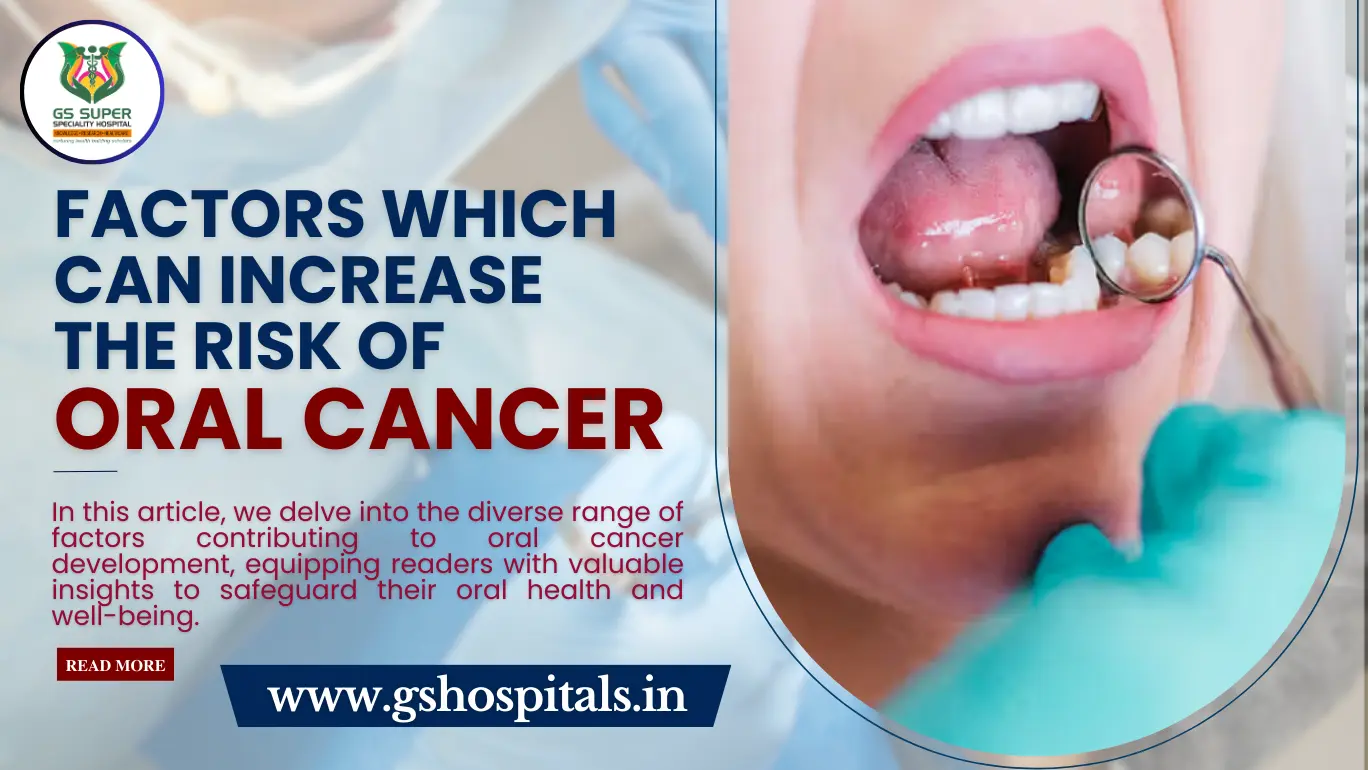
Oral cancer poses a significant threat to individuals globally, emphasizing the importance of recognizing its associated risk factors. By comprehending these factors, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate their risk, leading to improved prevention, early detection, and treatment outcomes. In this article, we delve into the diverse range of factors contributing to oral cancer development, equipping readers with valuable insights to safeguard their oral health and well-being.
Exploring Lifestyle Factors
Tobacco Use
Smoking : Inhalation of tobacco smoke exposes the oral tissues to a multitude of carcinogens, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nitrosamines. These substances can cause DNA damage in the cells lining the oral cavity, leading to the development of oral cancer.
Smokeless Tobacco : Chewing tobacco and snuff are popular forms of smokeless tobacco that pose a significant risk for oral cancer. The prolonged contact of these products with the oral mucosa exposes the tissues to high concentrations of harmful chemicals, increasing the likelihood of cancerous changes.
Alcohol Consumption
Chronic and heavy alcohol consumption is strongly associated with an elevated risk of oral cancer, particularly when combined with tobacco use. Alcohol can act as a solvent, facilitating the penetration of carcinogens into the oral tissues and promoting cellular damage.
The synergistic effect of alcohol and tobacco further exacerbates the risk, as alcohol can enhance the carcinogenic effects of tobacco and impair the body's ability to repair damaged DNA.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Oral Cancer Risk
Tobacco use and alcohol consumption are the primary modifiable risk factors for oral cancer, accounting for a significant proportion of cases worldwide. The harmful substances present in tobacco smoke and alcoholic beverages can induce genetic mutations and disrupt cellular processes, paving the way for cancer development.
Preventive Measures
Smoking Cessation : Quitting smoking and other forms of tobacco use is the single most effective way to reduce the risk of oral cancer. Support programs, nicotine replacement therapies, and counseling can aid individuals in overcoming tobacco addiction.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption : Limiting alcohol intake to moderate levels can help mitigate the risk of oral cancer. Guidelines recommend no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices : Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular physical activity, can bolster the body's defenses against cancer. Maintaining optimal oral hygiene and attending regular dental check-ups are also integral components of oral cancer prevention.
Exploring Dietary Habits
Poor Nutrition
A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables, which are abundant sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, is associated with an elevated risk of oral cancer. These nutrient-rich foods play crucial roles in supporting immune function, combating oxidative stress, and maintaining cellular health.
The absence of essential nutrients, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and folate, in the diet can impair immune responses and hinder the body's ability to suppress the growth of cancerous cells.
Additionally, inadequate intake of dietary fiber from plant-based foods may contribute to digestive issues and alterations in gut microbiota, potentially influencing cancer development in the oral cavity.
Impact of Poor Nutrition on Oral Cancer Risk
Poor dietary habits characterized by the insufficient consumption of fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-dense foods can compromise overall health and increase susceptibility to oral cancer. The deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals weakens immune defenses, leaving the body vulnerable to the proliferation of cancer cells.
Preventive Measures
Balanced Diet : Emphasize a diverse and balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Aim to incorporate colorful produce into meals to maximize nutrient intake and antioxidant protection.
Nutrient-Rich Foods : Prioritize foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as selenium, zinc, and phytonutrients, which have been linked to lower cancer risk. Examples include citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption : Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive intake can deplete nutrient stores and impair nutrient absorption in the body. Choose water or non-alcoholic beverages as alternatives to alcoholic drinks.
Supplementation : In cases where dietary intake may be inadequate, consider supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Multivitamin supplements or specific nutrient supplements can help bridge nutritional gaps and support overall health and immune function.
Exploring Oral Hygiene Practices
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting essential oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can significantly elevate the risk of oral cancer. Inadequate oral care fosters an environment conducive to the proliferation of harmful bacteria and the development of oral infections, inflammation, and other pathological conditions.
The accumulation of dental plaque and tartar on teeth and along the gumline provides a reservoir for bacteria to thrive, leading to chronic periodontal (gum) disease. Periodontal pathogens and inflammatory mediators can infiltrate oral tissues, promoting cellular damage, DNA mutations, and cancerous changes within the oral cavity.
Impact of Poor Oral Hygiene on Oral Cancer Risk
Poor oral hygiene practices compromise the integrity of the oral mucosa and create favorable conditions for microbial colonization and inflammation. Persistent bacterial infections and chronic inflammatory responses perpetuate tissue damage and facilitate carcinogenic processes, increasing susceptibility to oral cancer development.
Preventive Measures
Routine Oral Care : Establish and maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine that includes brushing teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing between teeth to remove plaque and debris. Additionally, use antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacterial load and minimize oral inflammation.
Professional Dental Visits : Schedule regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings with a dentist or dental hygienist at least twice a year. These visits allow for early detection and treatment of oral health issues, including periodontal disease and oral cancer precursors.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits : Adopt lifestyle habits that promote oral and overall health, such as avoiding tobacco products, limiting alcohol consumption, consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
Self-Examination : Perform monthly self-examinations of the oral cavity, including the lips, gums, tongue, cheeks, and roof of the mouth, to monitor for any unusual changes or abnormalities. Report any persistent sores, lumps, red or white patches, or other concerning symptoms to a dental or healthcare professional promptly for evaluation.
Preventive Measures
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
Several strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), notably HPV-16 and HPV-18, have emerged as significant risk factors for oral cancer, particularly in the oropharyngeal region.
HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can infect the cells of the oral cavity, including the lining of the mouth and throat. Upon infection, HPV can integrate into the host cell's DNA, disrupting normal cellular processes and promoting uncontrolled cell growth.
The presence of high-risk HPV strains, such as HPV-16 and HPV-18, in oral mucosal tissues has been linked to the development of premalignant lesions and invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), a common form of oral cancer.
Individuals with a history of high-risk sexual behaviors, multiple sexual partners, or oral-genital contact are at increased risk of HPV infection and subsequent oral cancer development.
Additionally, immunocompromised individuals, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or undergoing organ transplantation, may be more susceptible to persistent HPV infections and the progression to oral cancer.
Impact of HPV on Oral Cancer Risk
HPV-mediated oral cancers often exhibit distinct clinical and molecular characteristics compared to non-HPV-associated oral malignancies. These tumors typically arise in the oropharyngeal region, including the tonsils, base of the tongue, and soft palate, and are more prevalent among younger individuals with no history of tobacco or alcohol use.
Preventive Measures
Vaccination : The HPV vaccine, available for both males and females, provides protection against infection with high-risk HPV strains, including HPV-16 and HPV-18. Routine vaccination during adolescence or early adulthood can effectively prevent HPV-related oral and other cancers.
Safe Sexual Practices : Practicing safe sexual behaviors, including limiting the number of sexual partners and using condoms or other barrier methods during oral-genital contact, can reduce the risk of HPV transmission and oral cancer acquisition.
Regular Screening : Routine oral cancer screenings by dental and healthcare professionals can facilitate early detection of oral lesions and abnormalities associated with HPV infection. Timely identification allows for prompt intervention and treatment, improving outcomes for individuals at risk of HPV-related oral cancers.
Genetic Factors and Chronic Health Conditions on Oral Cancer Risk
Genetic Factors
Individuals with a family history of oral cancer or other malignancies may harbor genetic predispositions that elevate their susceptibility to developing the disease.
Genetic mutations and hereditary factors inherited from parents or close relatives can contribute to an increased risk of oral cancer manifestation.
Genetic studies have identified several hereditary syndromes associated with a higher incidence of oral cancer, including Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Fanconi anemia, and dyskeratosis congenita.
Individuals with a familial predisposition to oral cancer may benefit from enhanced surveillance and early detection strategies to monitor for signs of disease development and initiate timely interventions.
Chronic Health Conditions
Chronic irritation or trauma to the oral mucosa is recognized as a potential risk factor for oral cancer initiation and progression.
Conditions that induce persistent irritation or inflammation of the oral tissues, such as ill-fitting dentures, sharp teeth, or abrasive dental appliances, can increase the likelihood of cellular damage and malignant transformation.
Prolonged exposure to irritants or abrasive agents can induce genetic alterations and disrupt cellular homeostasis, fostering an environment conducive to the development of cancerous lesions.
Regular assessment and management of chronic oral irritations by dental professionals are essential to mitigate the risk of oral cancer development. Individuals experiencing chronic oral discomfort or trauma should seek prompt evaluation and intervention to address underlying factors contributing to tissue irritation and reduce the likelihood of malignant transformation.
Genetic and Chronic Health Factors Interaction
The interplay between genetic predisposition and chronic health conditions underscores the multifactorial nature of oral cancer etiology. While genetic factors may confer inherent susceptibility to disease development, environmental exposures and lifestyle habits, such as chronic oral irritation, can exacerbate this risk. Comprehensive risk assessment incorporating both genetic and environmental determinants is critical for identifying high-risk individuals and implementing targeted preventive measures and surveillance protocols.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the importance of cholesterol ratio is paramount for assessing cardiovascular risk and maintaining heart health. By evaluating the balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol levels, cholesterol ratio provides valuable insights into the risk of heart disease and stroke. Monitoring cholesterol ratio, along with other lipid parameters, allows healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans and preventive strategies to reduce cardiovascular risk.
Best Cancer Hospital in Hapur at GS Hospital, we are committed to raising awareness about oral cancer risk factors and providing comprehensive screening, diagnosis, and treatment services for patients at risk. Our team of experienced oncologists the Best Oncologist in Meerut, dentists, and healthcare professionals is dedicated to promoting oral health and early detection of oral cancer. By addressing modifiable risk factors and advocating for regular dental check-ups and screenings, we can work together to reduce the burden of oral cancer and improve outcomes for patients.
If you have any questions or concerns about oral cancer risk factors or would like to schedule a screening or consultation, please don't hesitate to contact GS Hospital. Your oral health is our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQs
1. What screening and diagnostic services does GS Hospital offer for oral cancer detection?
Cancer Specialist in Ghaziabad at GS Hospital, we offer comprehensive screening and diagnostic services for oral cancer detection, including oral examinations, biopsy procedures, imaging tests (such as X-rays and CT scans), and HPV testing. Our multidisciplinary team of oncologists and dentists ensures timely and accurate diagnosis for patients at risk of oral cancer.
2. How does GS Hospital educate patients about oral cancer prevention and early detection?
GS Hospital conducts educational programs, seminars, and awareness campaigns to educate patients about oral cancer prevention, risk factors, and early detection. We provide information about lifestyle modifications, including tobacco cessation, alcohol moderation, and healthy dietary habits, to reduce the risk of oral cancer. Additionally, we encourage regular dental check-ups and screenings to detect any suspicious oral lesions early.
3. Does GS Hospital offer specialized treatment options for oral cancer management?
Yes, GS Cancer Hospital Ghaziabad provides specialized treatment options for oral cancer management, tailored to each patient's individual needs and preferences. Our comprehensive approach may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and supportive care services. We prioritize patient-centered care and collaborate closely with other healthcare professionals to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and quality of life for our patients.
4. What supportive services does GS Hospital offer for oral cancer patients and their families?
Best Oral Cancer Hospital in Ghaziabad at GS Hospital offers a range of supportive services for oral cancer patients and their families, including nutritional counseling, pain management, psychosocial support, and survivorship programs. Our dedicated team of oncology nurses, social workers, and support staff provides compassionate care and guidance throughout the treatment journey, addressing the physical, emotional, and practical needs of patients and their loved ones.
5. How can patients schedule an appointment or seek further information about oral cancer services at GS Hospital?
Patients can schedule an appointment or seek further information about oral cancer services at GS Hospital by contacting our oncology department or visiting our website. Our friendly and knowledgeable staff are available to assist with appointment scheduling, answer any questions, and provide guidance on accessing our comprehensive oral cancer care services. Your health and well-being are our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way.